Effects of Stimulants
Stimulants affect the way that the brain works by causing changes in the ways in which the nerve cells communicate with one another. These cells, called neurons, are responsible for transmitting messages throughout the body and acting as the gateways for pain response, energy, behavior and attitude. When stimulants are taken, they produce stimulating effects on the central nervous system which causes pleasure, increased energy and various other effects.
Euphoric Effects
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, the most common effects of stimulants are euphoria and pleasure. The euphoric effects of stimulants are the result of the substance disrupting the regular functioning of the brain causing an abrupt increase in the production of dopamine. Dopamine is the chemical in the brain that is responsible for producing pleasure, happiness and euphoria.
Unfortunately, repeat use of stimulants can cause opposite effects. The user may no longer feel euphoria when he or she takes the drug as a result of a dopamine production that was once so overloaded that it has not ceased all together. As a user becomes addicted to stimulants, he or she will often feel as if the only way to be happy or to feel good is by taking stimulants.
Short Term Effects of Stimulants

Blurred vision and confusion are common short term effects of stimulants.
When the user first starts taking stimulants, he or she will feel energetic and joyous. The drug will cause increased alertness and energy. The user may even feel less hungry thanks to the stimulating effects of the drug. Additional short term effects of stimulants include:
- increased heart rate
- increased body temperature
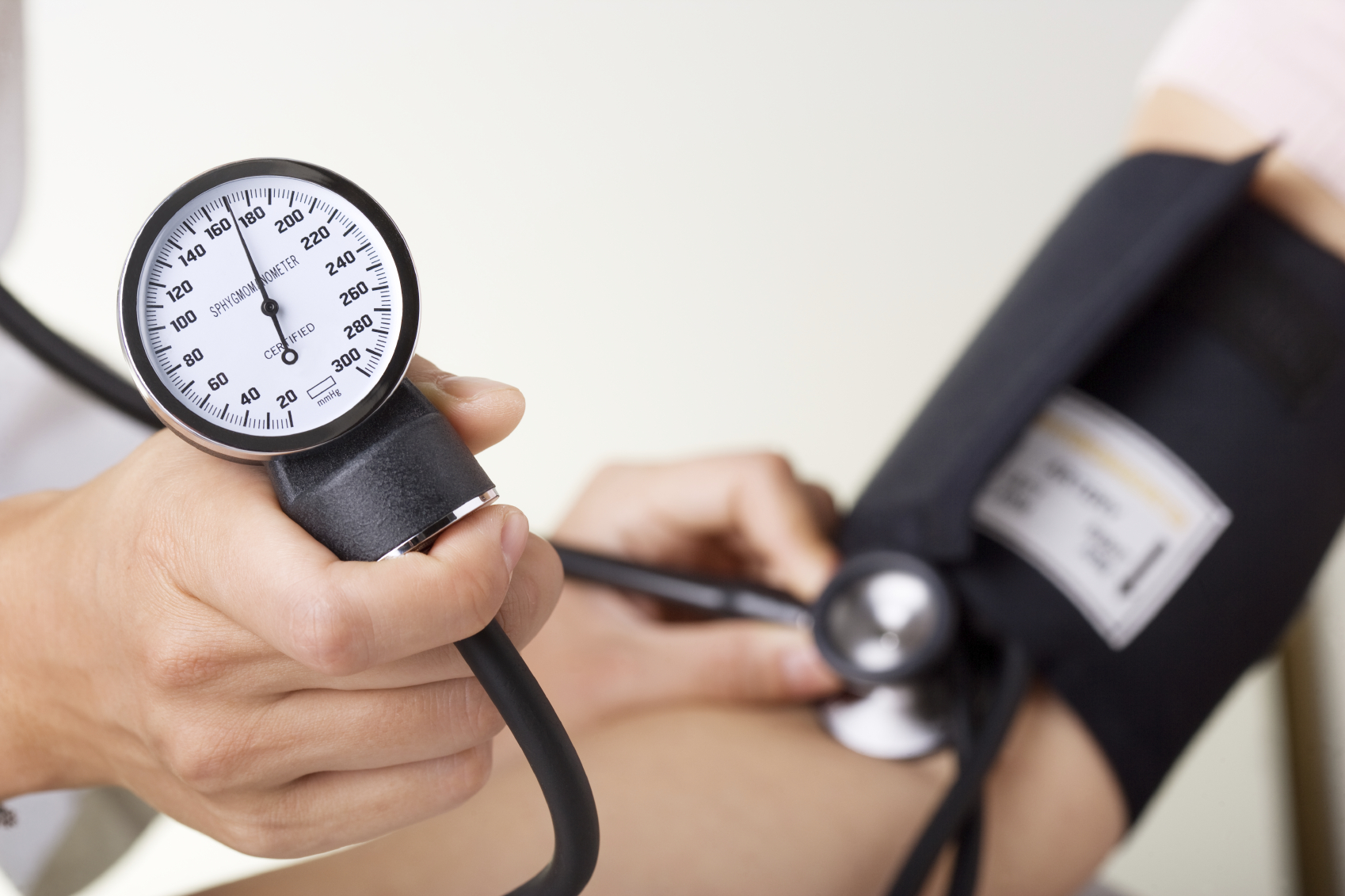
- increased blood pressure
- nausea
- blurred vision
- dilated pupils
- confusion
- muscle spasms
Stimulants will cause the heart to go into overtime, working diligently to pump blood throughout the body. This can cause serious consequences as the user is at an increased risk for heart attack or stroke when he or she is under the influence of stimulating drugs.
Long Term Effects of Stimulants
Stimulants have a wide potential to cause tolerance and dependence. Stimulant addiction can lead to overdose, permanent side effects or even death. Repeated use of the drug, whether a legal stimulant or an illegal stimulant, will likely lead to an increased tolerance that makes it difficult for the user to produce the same effects with the drug because he or she develops a resistance to it which requires them to use more and more with each attempt.
The long term effects of stimulants vary based on the type of stimulants being used, the user him or herself and various other factors. Potential long term effects of stimulants may include:
- anorexia or extreme weight loss
- hallucinations
- paranoia or anxiety
- difficulty concentrating or focusing
- dental problems
Depending on how the stimulants are being used, various physical effects of stimulants may also arise from such use. If a user is snorting cocaine, a dangerous stimulant, he or she may suffer from various effects including a chronic runny nose, nosebleeds, sinus infections or a loss of sense of smell. Stimulants that are injected may lead to infection at the injection site, transmission of disease such as HIV or Hepatitis from sharing dirty needles, or permanent scarring.
The long term effects of stimulants may also include permanent panic attacks, psychosis, or mental instability. People who abuse stimulants are at increased risk of contracting a number of diseases including STDs and may also suffer from adverse effects such as loss of sexual function, serious depression or delusions.
Calls to the general helpline will be answered by a paid advertiser. By calling the helpline you agree to our terms of use.