10 Symptoms of Stimulant Addiction You Can’t Miss
Stimulant addiction is often overlooked or mistaken as something else. If you notice someone you love showing any of these signs of misuse, abuse or potential dependence on stimulants, consider seeking immediate help.
1. Depression
In long-term stimulant abuse, depression is one of the most common symptoms that clearly shows the individual has a problem. While cocaine, amphetamines, and other stimulant drugs can cause a boost in mood and energy for the time they are in an individual’s system, the crash afterward can cause feelings of sadness, fatigue, or hopelessness. However, over time, this pattern can develop into an even more dangerous issue, often causing the individual to show signs of severe, clinical depression.
2. Malnutrition
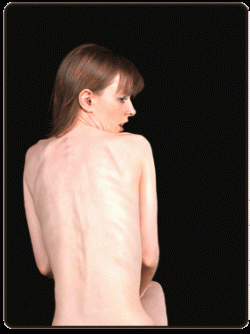
Stimulant addiction can cause extreme weight loss.
When someone abuses stimulants in high doses consistently over a long period of time, they will likely become malnourished and undergo extreme weight loss. This occurs because “many chronic cocaine [and other types of stimulant drug] users lose their appetite” because the drugs suppress it (NIDA). Then, when the individual stops eating, they can become extremely sick and experience a host of other problems, many of them gastrointestinal issues.
3. Intense Cravings
Experiencing intense cravings whenever you do not abuse stimulant drugs is a strong symptom of addiction. This is because the cravings caused by these substances are often much more intense and last longer than those caused by other types of drugs. According to the NLM, “In the past, people underestimated how addictive cocaine can be. However, cocaine is addictive when addiction is defined as a desire for more of the drug, despite negative consequences.”
All stimulant drugs have this same effect where the desire for the drug outweighs any negative consequences, and this desire can last long after treatment has ended. If you are already experiencing intense cravings for stimulants, you are addicted and should receive treatment now in order to work on controlling this issue.
4. Mania
Especially with the abuse of prescription stimulant drugs (such as Adderall, Concerta, and Ritalin), mania can occur when someone takes these drugs in large doses. The individual will act bizarrely, possibly being extremely happy one moment and then angry or aggressive the next. They will become very talkative and have an inflated self-esteem as well as becoming easily distracted and concerned with pleasurable pursuits.
In those who are prescribed stimulant drugs, the effects of these substances help them with this exact issue and can calm symptoms of ADHD, causing them to become more focused and less flighty. However, those who abuse these drugs in large doses will begin to act exactly the way the drug is attempting to prevent them from acting. A consistent issue of this type points to stimulant addiction.
5. Disturbed Sleep Patterns
When someone becomes addicted to these drugs, their sleep patterns become extremely erratic. This is because they will often abuse the drug in a binge pattern, trying to hold on to their high as long as possible. This will cause them to go without sleep for days on end. Then, when they do finally stop, they will crash and sleep for a long period of time. These disturbed sleep patterns are a sign of binge-crash abuse which can lead directly to addiction.
6. Paranoia
Stimulants do not only cause a person to feel good or happy all the time; on the contrary, cocaine can cause long-term users to “become angry, nervous, and afraid that someone’s out to get [them]” (NLM). This issue of paranoia can begin with a person’s first time abusing stimulants but will only become worse the longer this dangerous abuse goes on.
In fact, many users become so paranoid over long-term abuse that they begin to display signs of a schizophrenia-like disorder called toxic psychosis. This condition is extremely dangerous, and anyone who experiences it needs treatment for stimulant addiction immediately.
7. Tolerance and Sensitization
Becoming tolerant to the stimulant drug you abuse is a sure sign that you are addicted. Over time, the drug will not cause the same effects that it once did when taken at the same dosage level. You will begin to feel that you need to take more of the substance each time you abuse it in order to feel the same effects.
This kind of tolerance goes hand-in-hand with addiction but can also lead to overdose. In addition, taking higher doses each time you abuse the drug can lead to sensitization to the drug’s “anxiety-producing, convulsant, and other toxic effects” (NIDA). While you build up a tolerance for the pleasant effects of the drug, you will become more sensitive to its unpleasant effects.
8. Crank/Coke Bugs
A terrifying hallucination that is commonly experienced by those who abuse incredibly high doses of these drugs, methamphetamine abuse and cocaine abuse can cause an individual to experience crank bugs or coke bugs respectively. As stated by CESAR, this is “the tactile hallucination” that bugs are burrowing under the user’s skin. While it is also part of toxic psychosis, it can be easily identified by the fact that users will often have open sores or skin infections from picking at these imaginary bugs. It is a clear sign of stimulant addiction and one that requires treatment.
9. Inability to Experience Pleasure
The inability to feel pleasure, from any source except perhaps the drug itself, is another strong symptom of addiction. In some cases, people do not even feel the pleasurable effects of the drug anymore once they have reached this state. Still, users will continue to take the drug of their choice because
- They don’t want to experience any of the withdrawal symptoms.
- Their cravings are still too intense.
- They will only be able to function when under the influence of the drug.
10. Drug-Seeking Behavior
Stimulants can cause intense drug-seeking behavior in those who abuse them, to the point where the individual will be willing to do anything in order to get more of the drug. This type of drug-seeking behavior may include:
- Putting themselves or someone else in danger in order to get more of the drug
- Stealing or faking prescriptions when they cannot obtain more prescription stimulants otherwise
- Taking drugs from someone they do not trust
Individuals addicted to stimulants will be willing to do anything to get more, even if that act is illegal, dangerous, or life-threatening.